
موقع د. كمال سيد الدراوي
طبي_ اكاديمي _ ثقافي _ تعليمي _ _ استشارات طبية_فيديو طبي
|
|
| | كل يوم معلومه أساسيه |  |
| | |
| كاتب الموضوع | رسالة |
|---|
د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الإثنين أكتوبر 30, 2023 5:08 pm الإثنين أكتوبر 30, 2023 5:08 pm | |
| What is the frequency of ultrasound?
In physics the term “ultrasound” applies to all acoustic energy with a frequency above human hearing (20,000 hertz or 20 kilohertz). Typical diagnostic sonographic scanners operate in the frequency range of 2 to 18 megahertz, hundreds of times greater than the limit of human hearing.
...............................
When was ultrasound used in medicine?
1956
Invention of ultrasound
Well, in the year of 1956, ultrasound was first used for medical purposes. Glasgow was the place where it saw its first light. Besides, ultrasound was the brainchild of engineer Tom Brown and Obstetrician Ian Donald. They were the first people who crafted the prototype system.
....................................
What is the first use of ultrasound?
The History of Ultrasound | BMUS
The use of ultrasound in medicine began during and shortly after the 2nd World War in various centres around the world. The work of Dr. Karl Theodore Dussik in Austria in 1942 on transmission ultrasound investigation of the brain provides the first published work on medical ultrasonics.
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الثلاثاء يوليو 30, 2024 11:33 am عدل 2 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الإثنين أكتوبر 30, 2023 5:19 pm الإثنين أكتوبر 30, 2023 5:19 pm | |
|  Abstract. Ultrasound is a form of non-ionizing radiation that uses high-frequency sound waves to image the body. It is a real-time investigation which allows assessment of moving structures and also facilitates measurement of velocity and directionality of blood flow within a vessel................................................. Abstract. Ultrasound is a form of non-ionizing radiation that uses high-frequency sound waves to image the body. It is a real-time investigation which allows assessment of moving structures and also facilitates measurement of velocity and directionality of blood flow within a vessel.................................................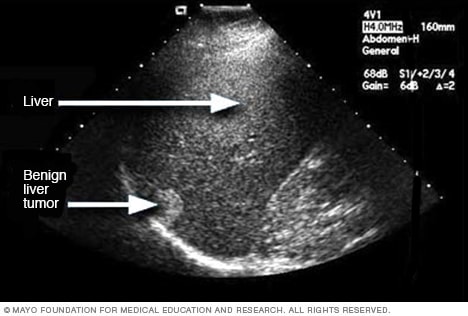 What is diagnostic ultrasound?Diagnostic ultrasound, also called sonography or diagnostic medical sonography, is an imaging method that uses sound waves to produce images of structures within your body. The images can provide valuable information for diagnosing and directing treatment for a variety of diseases and conditions.Apr 30, 2022,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,What is M mode in ultrasound?Background: M-mode or "motion" mode is a form of ultrasound imaging that is of high clinical utility in the emergency department. It can be used in a variety of situations to evaluate motion and timing, and can document tissue movement in a still image when the recording of a video clip is not feasible. What is diagnostic ultrasound?Diagnostic ultrasound, also called sonography or diagnostic medical sonography, is an imaging method that uses sound waves to produce images of structures within your body. The images can provide valuable information for diagnosing and directing treatment for a variety of diseases and conditions.Apr 30, 2022,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,What is M mode in ultrasound?Background: M-mode or "motion" mode is a form of ultrasound imaging that is of high clinical utility in the emergency department. It can be used in a variety of situations to evaluate motion and timing, and can document tissue movement in a still image when the recording of a video clip is not feasible.
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الأحد يونيو 23, 2024 3:11 pm عدل 2 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الإثنين أكتوبر 30, 2023 5:21 pm الإثنين أكتوبر 30, 2023 5:21 pm | |
| What is B-mode ultrasound?B-mode: In B-mode ultrasound, a linear array of transducers simultaneously scans a plane through the body that can be viewed as a two-dimensional image on screenWhat is the wavelength of an ultrasound?Ultrasound is defined by the American National Standards Institute as "sound at frequencies greater than 20 kHz". In air at atmospheric pressure, ultrasonic waves have wavelengths of 1.9 cm or lessWhat are the characteristics of ultrasound?Properties of ultrasound:- Ultrasonic waves cannot move in a vacuum.
- Ultrasonic waves constitute high-frequency, short-wavelength sound waves.
- These waves travel at the same velocity as sound in a particular medium.
- Throughout homogenous media, their velocity remains constant
- Does ultrasound use radiation?
Because ultrasound images are captured in real-time, they can also show movement of the body's internal organs as well as blood flowing through the blood vessels. Unlike X-ray imaging, there is no ionizing radiation exposure associated with ultrasound imaging.Sep 28, 2020
- What are the limitations of ultrasound?
Ultrasound is a valuable tool, but it has limitations. Sound waves don't travel well through air or bone, so ultrasound isn't effective at imaging body parts that have gas in them or are hidden by bone, such as the lungs or head. Ultrasound may also be unable to see objects that are located very deep in the human body.Apr 30, 2022
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الأحد يونيو 23, 2024 3:13 pm عدل 2 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الإثنين أكتوبر 30, 2023 5:36 pm الإثنين أكتوبر 30, 2023 5:36 pm | |
| Why is ultrasound used for pregnancy?
To check your baby's heartbeat, muscle tone, movement and overall development. To check to see if you're pregnant with twins, triplets or more (also called multiples) To check if your baby is in the heads-first position before birth. To examine your ovaries and uteru
Why is gel used in ultrasound?
Ultrasound gel is used as a coupling medium in all ultrasound procedures to replace air between the transducer and the patient's skin, as ultrasound waves have trouble in travelling through air
What is the source of the ultrasound?
Among the earliest known sources of ultrasound are those emanating from the animal kingdom. Dogs, birds, crickets, and bats are amongst those creatures whose communication signals extend beyond the range of human hearing. In addition bats use ultrasound as a guidance system between 50 and 100 kHz.
How are ultrasound images formed?
The ultrasound image is produced based on the reflection of the waves off of the body structures. The strength (amplitude) of the sound signal and the time it takes for the wave to travel through the body provide the information necessary to produce an image.
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الأحد يونيو 23, 2024 3:14 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الإثنين أكتوبر 30, 2023 5:50 pm الإثنين أكتوبر 30, 2023 5:50 pm | |
| What are the components of ultrasound?Ultrasound device, essentially, consists of a transducer, transmitter pulse generator, compensating amplifiers, the control unit for focusing, digital processors and systems for display.What kind of crystal is in ultrasound?piezoelectric crystalsThe first ultrasound transducers were made using natural piezoelectric crystals (quartz, Rochelle salts, tourmaline). Modern transducers use synthetic crystals, such as PZT (lead zirconate titanate), that have high density, velocity, and acoustic impedance.What are the types of probes?We'll explain some of the most popular ones below in detail.- Linear Probe. Linear probes have a flat array and appearance. ...
- Convex Probe. ...
- Endocavitary Probe. ...
- Phased Array/Cardiac Probe. ...
- Transesophageal (TEE) Probe (trans esophageal echocardiography). ...
- 3D/4D Probe.
- What is C mode ultrasound?
C-Mode functions similarly to B-Mode, although it has not been been as developed to full potential. Using data and a range of depth from A-Mode, the transducer then moves to B-Mode (or 2D mode) and examines the whole region at the depth originally employed in two dimensional imagery
- .
C-mode imaging is one of the ultrasound imaging modalities. Compared with other modalities, e.g. A-mode, B-mode, M-mode, and Doppler, C-mode is mainly developed and used in industry testing. The potential of C-mode imaging for medical application has not been fully explored
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الأحد يونيو 23, 2024 3:16 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 | |   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 | |   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الثلاثاء أكتوبر 31, 2023 6:02 pm الثلاثاء أكتوبر 31, 2023 6:02 pm | |
| What radiopaedia means
Radiopaedia - Wikipedia
Radiopaedia is a wiki-based international collaborative educational web resource containing a radiology encyclopedia and imaging case repository
What is the basic principle of ultrasound?
The sound waves are reflected back to the transducer by boundaries between tissues in the path of the beam (e.g. the boundary between fluid and soft tissue or tissue and bone). When these echoes hit the transducer, they generate electrical signals that are sent to the ultrasound scanner
What is the physics of ultrasound?
Ultrasound transducers contain piezoelectric crystals that, when electrical impulses are applied, produce waves at frequencies determined by the crystal's propagation speed, divided by two times the thickness of the crystal layer. The typical thickness of crystal layers is between 0.2mm and 2mm.Mar 27, 2023
What is nature of ultrasound?
THE NATURE OF ULTRASOUND
Ultrasonic waves are waves of frequency above the audible frequencies of the human ear. In medical diagnostics are used ultrasound frequencies between 3 and 10 MHz.
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الأحد يونيو 23, 2024 3:28 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الثلاثاء أكتوبر 31, 2023 7:05 pm الثلاثاء أكتوبر 31, 2023 7:05 pm | |
| What is the difference between embryo and fetus radiopaedia?
An embryo (plural: embryos) is the term given to the precursor of a fetus and in humans the embryonic period is usually considered to be between the first (1st) and the eighth (8th) week (eleventh week according to some reports) of development after fertilisation.Mar 5, 2021
US WAVE RANGE
Ultrasound is defined by the American National Standards Institute as "sound at frequencies above those audible to the human hearing (greater than 20 kHz").
In air at atmospheric pressure, ultrasonic waves have wavelengths of 1.9 cm or less
Ultrasound typically used in clinical settings has frequencies between 2 and 12 MHz..
US waves are
Typically 1 or 3 MHz... WAVELENGTH is the distance
between two equivalent points on the waveform in the particular medium.
In an 'average tissue' the wavelength @ 1MHz would be 1.5mm and @ 3 MHz would be 0.5 mm.
The frequencies used in ultrasonic diagnosis are in the range of 1 to 10 MHz. The speed of sound waves in the tissues of the human body averages about 1540 m/s (close to that for water). So, the wavelength of a 1 MHz wave is about λ=v/f=1540/1∙106=1.5∙10–3m=1.5mm Mhz - 6 x 10 *6/s........
Frequencies used in USG range from 2 to 18 MHz. Frequency ( f ) is inversely proportional to wavelength ( λ )
and varies according to the specific velocity of sound in a given tissue ( c ) according to the formula: λ = c / f
What is the formula for wavelength frequency in US?
Frequencies used in
ultrasonography range from 2 to 18 MHz. Frequency ( f ) is inversely proportional to wavelength ( λ ) and varies according to the specific velocity of sound in a given tissue ( c ) according to the formula: λ = c / f
What is the formula for US waves ?
Velocity of ultrasonic waves in a medium (V):
(V) = f x l OR Where f = is Number of cycles per second & is called frequency. Measured in 'Hertz'. Abbreviated as 'Hz'.
One Hertz is equivalent to One cycle per second l = Distance covered in one cycle is wavelength V= Velocity of Ultrasonic wave inside the medium in 'mm/s' 2.
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الأحد يونيو 23, 2024 3:29 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الثلاثاء أكتوبر 31, 2023 7:15 pm الثلاثاء أكتوبر 31, 2023 7:15 pm | |
| What is the formula of ultrasound wave?
The product of the frequency (ν) and the wavelength (λ) is the velocity of the wave; that is, c = νλ. In most soft tissues, the velocity of ultrasound is about 1540 m/sec. Frequencies of 1 MHz and greater are required to furnish ultrasound wavelengths suitable for diagnostic imaging
What is the frequency and wavelength of ultrasound?
The velocity of sound in biologic tissue is a constant at approximately 1540 meters/second. Applying a frequency of 2 MHz of ultrasound energy will result in a wavelength of 0.77 mm, whereas applying a frequency of 8 MHz of ultrasound energy will result in a wavelength of 0.19 mm
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الأحد يونيو 23, 2024 3:30 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 | |   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الثلاثاء أكتوبر 31, 2023 9:04 pm الثلاثاء أكتوبر 31, 2023 9:04 pm | |
| Basic physics for generation of US image ?
Brightness mode (B mode) is the basic mode that is usually used. Ultrasound waves are emitted from piezoelectric crystals of the ultrasound transducer. Depending on the acoustic impedance of different materials, which depends on their density, different grades of white and black images are produced
what is the speed of US ?
The soeed of US In diagnostic ultrasound imaging the speed of sound is assumed to be 1540 m/s in soft tissues ;
330 m/s in air
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الأحد يونيو 23, 2024 3:32 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الأربعاء نوفمبر 01, 2023 6:44 pm الأربعاء نوفمبر 01, 2023 6:44 pm | |
| Can ultrasound detect fertilization?
Fertilised egg is an egg which has fused with d sperm. That's a microscopic structure and hence can't be seen on scan.Nov 16, 2017
Why are ovaries not visible on ultrasound?
Sometimes imaging with ultrasound, MRI or CT can have a hard time identifying ovaries for a multitude of reasons, with the most common being menopausal ovaries or lots of gas in the bowel, which can hide the ovaries
Can ultrasound cause bleeding?
Pelvic exam or ultrasound: Your cervix can bleed after a pelvic exam or transvaginal ultrasound because it's highly sensitive (due to increased hormones).Nov 17, 2021
Which day of period is best for ultrasound?
Information to prepare for your ultrasound
A scan can be performed at any stage of the cycle. If you are menstruating regularly, the best time for an ultrasound is from day 5 to day 11 of the menstrual cycle (counting from the first day of your period) especially if there is bleeding between your periods.
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الأحد يونيو 23, 2024 3:34 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 | |   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الأربعاء نوفمبر 01, 2023 7:02 pm الأربعاء نوفمبر 01, 2023 7:02 pm | |
| When is pregnancy visible in ultrasound?
How soon can you see a baby on an ultrasound? Pregnancy care providers can detect an embryo on an ultrasound as early as six weeks into the pregnancy. An embryo develops into a fetus around the eighth week of pregnancy.Sep 28, 2022
Can ultrasound detect after ovulation?
The corpus luteum is responsible for producing all that amazing progesterone. A pelvic ultrasound can detect the presence of the corpus luteum in the ovary after ovulation has occurred.Dec 22, 2021.
Can ultrasound detect hidden pregnancy?
Sometimes an ultrasound can miss the fetus in the womb. Typically, health care providers use ultrasound imaging to check for pregnancy in the early stages – between 10 and 13 weeks gestation. It's unlikely to detect a heartbeat by ultrasound before the seventh week of pregnancy.Apr 30
Are ovarian cysts visible on ultrasound?
An ultrasound can pinpoint the location, size, and makeup of ovarian cysts. Abdominal ultrasound and vaginal ultrasound can evaluate ovarian cysts. With an abdominal ultrasound, a technician moves a sensor over a woman's lower abdomen. A vaginal ultrasound uses a probe inserted inside the vagina
What is endometriosis ultrasound?
An endometriosis ultrasound is an imaging procedure that helps your provider determine if you have endometriosis. With endometriosis, pieces of tissue that line your uterus (endometrium) can appear in places outside your uterus, like your ovaries, bladder, and intestines.Sep 20, 2021
What is the normal size of ovary?
The normal size of a healthy ovary is 30 mm long, 25 mm wide, and 15 mm thick. In other words, the normal ovary size is 3 cm long, 2.5 cm wide, and 1.5 cm thick (0.8-12.7cc). In a healthy and normal-sized
ovary, the number of egg reserves are likely sufficient.
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الأحد يونيو 23, 2024 3:36 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الأربعاء نوفمبر 01, 2023 7:31 pm الأربعاء نوفمبر 01, 2023 7:31 pm | |
| What is previa in pregnancy?Placenta previa is a condition in which the placenta lies very low in the uterus and covers all or part of the opening to the cervical opening that sits at the top of the vagina. Placenta previa happens in about 1 in 200 pregnancies.What are 3 causes of bleeding in early pregnancy?What causes bleeding or spotting early in pregnancy?- Having sex.
- An infection.
- Implantation. ...
- Hormone changes. ...
- Changes in your cervix. ...
- Certain types of testing during pregnancy like an amniocentesis or Chorionic villus sampling (CVS). ...
- Problems related to smoking.
- Miscarriage is the sudden loss of a pregnancy before the 24th week. About 10% to 20% of known pregnancies end in miscarriage. But the actual number is likely higher. This is because many miscarriages happen early on, before people realize they're pregnant
- How is a miscarriage confirmed?
An ultrasound scan diagnoses most miscarriages. It may also diagnose miscarriages where some of the pregnancy remains in your womb. You might not be referred for an ultrasound if you: take a pregnancy test which gives a negative result
- You can ovulate and become pregnant as soon as two weeks after a miscarriage. Once you feel emotionally and physically ready for pregnancy after miscarriage, ask your health care provider for guidance. After one miscarriage, there might be no need to wait to conceive
- The symptoms of miscarriage can include:
Bleeding from the vagina with or without pain, including light bleeding called spotting.
Pain or cramping in the pelvic area or lower back.
Fluid or tissue passing from the vagina.
Fast heartbeat
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الأحد يونيو 23, 2024 3:38 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الأربعاء نوفمبر 01, 2023 8:18 pm الأربعاء نوفمبر 01, 2023 8:18 pm | |
| What are the types of miscarriage?
What are the types of miscarriage? There are several types of miscarriage — threatened, inevitable, complete, incomplete or missed. Other types of pregnancy loss include an ectopic pregnancy, molar pregnancy and a blighted ovum
What is the most common week to miscarry?
Most miscarriages - 8 out of 10 (80 percent) - happen in the first trimester before the 12th week of pregnancy. Miscarriage in the second trimester (between 13 and 19 weeks) happens in 1 to 5 in 100 (1 to 5 percent) pregnancies. Pregnancy loss that happens after 20 weeks is called stillbirth
What is a silent miscarriage?
missed (or silent) miscarriage is one where the baby has died or not developed, but has not been physically miscarried. In many cases, there has been no sign that anything was wrong, so the news can come as a complete shock
A missed miscarriage, also known as a missed abortion or a silent miscarriage, occurs when a fetus is no longer alive, but the body does not recognize the pregnancy loss or expel the pregnancy tissue. As a result, the placenta may continue to release hormones, so you may continue to experience signs of pregnancy.
Abortion is the medical term for a pregnancy loss before 20 weeks of gestational age. The types of spontaneous abortion include threatened, inevitable, incomplete, complete, septic, and missed abortion
What are the types of miscarriage?
Threatened miscarriage. When your body is showing signs that you might miscarry, that is called a 'threatened miscarriage'. ...
Inevitable miscarriage. ...
Complete miscarriage. ..
Incomplete miscarriage. ...
Missed miscarriage. ...
Recurrent miscarriage. ...
Expectant or natural management. ...
Medical management
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الإثنين يونيو 24, 2024 12:20 pm عدل 2 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الأربعاء نوفمبر 01, 2023 8:35 pm الأربعاء نوفمبر 01, 2023 8:35 pm | |
| What are the different types of miscarriage management?
Secondary care treatments options include expectant management (watchful waiting), medical management (with vaginal or oral misoprostol), or surgery. Following a miscarriage, the woman should be followed up in primary care and offered appropriate support, information, and advice
What is a miscarriage classified as?
Miscarriage is a naturally occurring event, unlike medical or surgical abortions. A miscarriage may also be called a "spontaneous abortion." Other terms for the early loss of pregnancy include: Complete abortion: All of the products (tissue) of conception leave the body.Nov 10, 2022
How many different types of pregnancy are there?
INTRAUTERINE PREGNANCY (NORMAL PREGNANCY) A normal pregnancy develops favorably when the embryo correctly implants into the lining of the uterus. ...
MULTIPLE PREGNANCY. ...
ECTOPIC PREGNANCY (EXTRAUTERINE) ...
MOLAR PREGNANCY.
What is the difference between abortion miscarriage and stillbirth?
The U.S. medical community most often defines miscarriage (also called spontaneous abortion) as the spontaneous loss of a nonviable, intrauterine pregnancy before 20 weeks gestational age (GA), while stillbirth (also called fetal death and intrauterine fetal demise) describes this event at ≥ 20 weeks GA.Dec 4, 2019
What is the difference between a missed abortion and an incomplete abortion?
The gestation would be termed a missed abortion only if the diagnosis of incomplete abortion or inevitable abortion was excluded. The condition may present as an anembryonic gestation (empty sac or blighted ovum) or as fetal demise prior to 20 weeks gestation
What is the difference between a threatened miscarriage and a miscarriage?
A threatened miscarriage is where there is vaginal bleeding during pregnancy. It does not always mean that you will go on to have a miscarriage; there is an 83% chance of your pregnancy continuing. If the pregnancy continues the bleeding will not cause any harm to the baby, even if the bleeding is heavy.
What is a clinical miscarriage?
The term clinical miscarriage is used when ultrasound examination or histological evidence has confirmed that an intrauterine pregnancy has existed. Clinical miscarriages may be subdivided into early clinical pregnancy losses (before gestational week 12) and late clinical pregnancy losses (gestational weeks 12 to 21).
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الإثنين يونيو 24, 2024 12:28 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الأربعاء نوفمبر 01, 2023 8:46 pm الأربعاء نوفمبر 01, 2023 8:46 pm | |
| What medication is used for missed miscarriage?
Two drugs are available to encourage the body to pass the baby: mifepristone and misoprostol. Since 2012, NICE has recommended using misoprostol alone for the medical management of missed miscarriage.Nov 13, 2020
What is the medical procedure to prevent miscarriage?
Cervical stitch (cerclage) may help prevent miscarriage due to a cervical factor, but has not been shown to benefit other women. The cervix (opening of the uterus) normally stays tightly closed during pregnancy. Occasionally it starts to open early, leading to miscarriage
What is a septic abortion?
Septic abortion is serious uterine infection during or shortly before or after a spontaneous or an induced abortion. Septic abortion is a gynecologic emergency. Septic abortions usually result from use of nonsterile techniques for uterine evacuation after induced or spontaneous abortion
Types of pregnancy include intrauterine pregnancy, ectopic pregnancy, tubal pregnancy, intra-abdominal pregnancy, singlet pregnancy, multiple pregnancy (twins, triplets, quadruplets, etc.), lupus pregnancy, high-risk pregnancy, and molar pregnancy. There are many different types of pregnancies.
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الإثنين يونيو 24, 2024 12:31 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الأربعاء نوفمبر 01, 2023 9:05 pm الأربعاء نوفمبر 01, 2023 9:05 pm | |
| What are the types of ectopic?
There are different types of ectopic pregnancies, which are tubal, cornual, cesarean scar, cervical, heterotopic, abdominal, and ovarian
What are the five pregnancy drugs categories?
FDA classifies various drugs used in pregnancy into five categories, categories A, B, C, D and X. Category A is considered the safest category and category X is absolutely contraindicated in pregnancy. This provides therapeutic guidance for the clinician.
What is the difference between abortion and intrauterine fetal death?
A death that occurs prior to 20 weeks' gestation is usually classified as a spontaneous abortion; those occurring after 20 weeks constitute a fetal demise or stillbirth
What is the difference between intrauterine death and miscarriage?
Intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD) is the medical term for a fetus that dies at or after the 20th week or second trimester of gestation. IUFD differs from a miscarriage, which occurs before the 20th week of pregnancy.Feb 2, 2023
How to differentiate between inevitable and incomplete abortion?
Inevitable abortion occurs when vaginal bleeding or rupture of membranes occur before 20 weeks gestation in the presence of cervical dilatation. Incomplete abortion typically occurs after 10 weeks gestation when the fetus is expelled and the placenta is retained in the uterus.
What antibiotics are used for incomplete abortion?
At present, all patients with incomplete abortions receive penicillin (a total of I.. 5 million units in 24 hours) on admission, since the number of induced abortions, symptoms of infection. or amount, of previous therapy can- not be reliably determined by history
What are the signs of abortion without bleeding?
Other symptoms of a miscarriage include:
back pain.
diarrhea.
nausea.
pelvic cramping (may feel like you're getting your period)
severe abdominal pain.
fluid coming from your vagina.
tissue coming from your vagina.
unexplained weakness
What is the best treatment for a threatened miscarriage?
There's nothing your provider can do to stop a miscarriage from occurring. Some pregnancy care providers prescribe progesterone, a hormone that supports a pregnancy. Low levels of progesterone may be a sign of a threatened miscarriage. You can take progesterone through injections, suppositories or tablets
What is progesterone in threatened abortion?
The symptoms of threatened miscarriage are vaginal bleeding, with or without abdominal pain, while the cervix of the womb is closed and the baby inside the womb is alive. Progesterone is a hormone that is known to prepare the uterus for implantation of the fertilized egg and suppress uterine contractions until term.
What is the difference between threatened and inevitable miscarriage?
Inevitable miscarriage is where women have unexplained vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain early in their pregnancies. Compared with a threatened miscarriage, an inevitable miscarriage is where the cervix opens in addition to the bleeding and pain.
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الإثنين يونيو 24, 2024 12:37 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الأربعاء نوفمبر 01, 2023 9:18 pm الأربعاء نوفمبر 01, 2023 9:18 pm | |
| What is the best treatment for a threatened miscarriage? There's nothing your provider can do to stop a miscarriage from occurring. Some pregnancy care providers prescribe progesterone, a hormone that supports a pregnancy. Low levels of progesterone may be a sign of a threatened miscarriage. You can take progesterone through injections, suppositories or tablets.Jun What is progesterone in threatened abortion? The symptoms of threatened miscarriage are vaginal bleeding, with or without abdominal pain, while the cervix of the womb is closed and the baby inside the womb is alive. Progesterone is a hormone that is known to prepare the uterus for implantation of the fertilized egg and suppress uterine contractions until term What are the clinical features of missed abortion? Clinical manifestations of missed abortion include absence of fetal heart tone, discharge from the breasts and diminution of their size, general fatigue, fever, and sometimes skin itch. Diagnosis of missed abortion is based upon the results of general and gynecologic examinations. What are 3 symptoms of a miscarriage? The symptoms can include: Bleeding from the vagina with or without pain, including light bleeding called spotting. Pain or cramping in the pelvic area or lower back. Fluid or tissue passing from the vagina. Fast heartbeat. What are the complications of a missed abortion? Echographic signs of missed abortion during the 1st trimester include absence of heart activity, absence of fetal movements, and changes in the size of the uterus, amniotic cavity, and embryo. The most frequent complications of missed abortion are uterine hemorrhage, infection, and malignant transformation. What painkillers are good for miscarriage? Take an over-the-counter pain medicine, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) for cramps. Talk to your doctor before you take ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve). Read and follow all instructions on the label. You may have cramps for several days after the miscarriage. What blood tests are done for miscarriage? Bleeding can also occur when the uterus or cervix stretches, which is common during pregnancy. Currently, to determine if a miscarriage is happening, blood tests to measure for a hormone produced by the placenta, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), are needed.Apr 25, 2022
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الإثنين يونيو 24, 2024 12:41 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الخميس نوفمبر 02, 2023 5:40 pm الخميس نوفمبر 02, 2023 5:40 pm | |
| What type of abortion is inevitable?
An inevitable abortion is defined as vaginal bleeding with progressive dilatation of the cervix but without expulsion of conception products before the twentieth week of
What is inevitable abortion?
Inevitable abortion is diagnosed in the presence of cramping, vaginal bleeding, an open cervical os on the physical exam but no passage of the products of conception. The intrauterine pregnancy may be either viable or nonviable on ultrasound.
inevitable VS incomplete abortion : Incomplete abortion typically occurs after 10 weeks gestation when the fetus is expelled and the placenta is retained in the uterus
classification of abortion Anembryonic pregnancy (formerly blighted ovum)
Nonviable pregnancy with a gestational sac, but with no yolk sac or embryo visualized on transvaginal ultrasonograph
Recurrent or habitual : ≥ 2 to 3 spontaneous abortions
Induced : Interruption of pregnancy with medications or a procedure
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الإثنين يونيو 24, 2024 12:47 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الخميس نوفمبر 02, 2023 5:58 pm الخميس نوفمبر 02, 2023 5:58 pm | |
| Classification of Abortion
Early
Abortion before 12 weeks gestation
Late
Abortion between 12 and 20 weeks gestation
Spontaneous
Pregnancy loss at < 20 weeks gestation
Threatened
Vaginal bleeding occurring before 20 weeks gestation without cervical dilation
Inevitable
Vaginal bleeding or rupture of the membranes before 20 weeks gestation accompanied by advanced dilation of the cervix
Incomplete
Dilation of cervix and expulsion of some products of conception
Complete
Closed cervix after expulsion of all products of conception
Missed
Death of an embryo or a fetus is confirmed, but there is no bleeding or cervical dilation and the products of conception have not been expelled…
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الإثنين يونيو 24, 2024 12:52 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: How to do ultrasound موضوع: How to do ultrasound  الخميس نوفمبر 02, 2023 8:38 pm الخميس نوفمبر 02, 2023 8:38 pm | |
| Choose a probe
Linear array probe: High-frequency (eg, 5 to 10 MHz) high-resolution image, little depth of penetration, flat footprint, rectangular image; choose for imaging superficial structures in detail (eg, for vascular cannulation or arthrocentesis)
Curvilinear probe: Low-frequency (eg, 1 to 5 MHz), lower-resolution image, greater depth of penetration, convex footprint, fanned image; choose for general imaging of deeper structures (eg, for E-FAST or aortic aneurysm evaluation)
Phased array probe: Typically low resolution and high depth, very small footprint that can fit in tight spaces (eg, between the ribs); often chosen specifically for cardiac imaging
Intracavity probe: Tight curvilinear probe, high frequency; choose for imaging within body cavities (eg, intraoral [peritonsillar tissues], transvaginal [ovaries], transrectal [prostate])
Probes typically have labels, such as a letter and number. The letter “C” stands for curved and “L” stands for linear. The adjacent numbers correspond to the probe’s frequency.How To Do Ultrasonography:
B (brightness) mode: This is the commonly used 2-dimensional imaging mode.
M (motion) mode: In M mode, the operator sees a one-dimensional image in the y-axis over time in the x-axis. The monitor shows 2 images: a single acoustic beam (solid line) imposed on the smaller B mode image on one portion of the monitor, and that single beam presented as a vertical line moving across the monitor in a separate M mode area. Motion, such as the beating of a heart, appears as repeating linear disturbances, and static structures create solid, undisturbed horizontal lines as the beam moves across the screen.
Color flow Doppler: This mode is diagnostic for the direction of blood flow. It also shows flow velocity. Red represents blood flow toward the transducer; blue represents blood flow away from it.
Probe: Select the probe you are using on the console.
Preset: If available on your machine, select the preset setting for the study you are doing (eg, obstetric, nerve, abdominal, cardiac).
Depth or frequency: Most machines allow adjustment for frequency. Adjust these to image the object of interest in the middle of the monitor. Unless it is determined by the preset, select the frequency on the machine console. This control may be labeled something other than “frequency,” such as “depth” (or “penetration”), or “resolution.” Examine deep structures first, then go superficial.
Focus: Most machines allow focus adjustment. Move the “x” mark on the side of the monitor to set the desired depth of focus.
Gain: Adjust the gain (brightness) so that fluids look black (anechoic), enhancing contrast with other solid, brighter (hyperechoic) structures. Automatic gain, or “autogain,” if available, sometimes helps clarify images, but sometimes results are better with manual adjustment. Some machines allow adjustment of gain separately at the top and bottom of the screen.
Dense objects, such as bone and stones, decrease the echogenicity of objects behind them (so there is usually a dark area behind them).
Conversely, hypoechoic objects act as “acoustic windows,” making objects behind them more echogenic and clear. For example, tissues behind a filled, hypoechoic bladder enhance brightly, and enhanced images of the heart are obtained by aiming the probe through the hypoechoic liver. Gain may need to be decreased to clearly image brightly enhanced objects.
Gas (eg, bowel gas) tends to give random, uninterpretable images, typically with mixed echogenicity due to mixed fluid and air. This is so-called dirty shadowing, with brighter images behind, caused by air.
Reverberation artifacts are common with curved or phased array transducers; they appear as parallel, equidistant lines (eg, within cysts or behind the pleura). One example of how to use them clinically is the comet tail, a type of vertical reverberation artifact created when the pleura rubs against the lung. Its absence suggests pneumothorax.
Freeze bar: Most machines have a freeze bar that captures the screen image and also have a roll-back feature that retrieves images from seconds earlier (eg, 3 seconds), in case an image of interest is inadvertently passed over.
Measurements: Machines typically have measurement capabilities (eg, labeled “measure” or sometimes “caliper”). For example, in some machines, freeze an image by pressing “freeze.” Move the monitor indicator to mark the beginning and the end points of the measurement and press “select.” The length between the marks is displayed on the upper left hand side of the monitor. Many machines can make calculations from measured values (eg, calculating bladder volume or estimated gestational age).
How To Do Ultrasonography: Maneuver the probe do ultrasound imaging
Standard probe orientation: With correct placement, the right side of the patient should appear
on the left side of the monitor. The probe orientation mark on one side of the probe should face the patient's right side (or cephalad if the probe is oriented longitudinally), and the marker dot on the ultrasound monitor is at the upper left corner of the ultrasound monitor.
Cardiac examination orientation: By selecting the cardiac preset, the marker dot will be on the right side of the monitor.
Coat the probe tip with ultrasound gel.
When using a covered probe, apply gel to the probe and then pull a glove or probe cover tightly over the probe tip to eliminate all air bubbles in the gel, and wrap rubber bands around the probe. Apply more gel in large amounts to the covered probe to ensure an adequate film as you move the probe.
Hold the probe and move it like a pen. Use your other fingers to stabilize the probe against the patient as you view the ultrasound monitor.
Optimize imaging. Try to avoid bone and gas, which are hyperechoic and can hide structures of interest. Gas can sometimes be pushed away. Optimize the imaging path to the target by using an acoustic window, generally through hypoechoic structures (eg, the liver when imaging the heart).
Begin by scanning large areas (sometimes called survey views) and then focus in to smaller areas of interest.
Slide the probe side-to-side or up or down, moving the probe footprint. With the footprint steady, you can tilt the probe, also called rocking, fanning, or sweeping, to give a more 3-dimensional view. You can compress the probe, pushing downward.
Rotate the probe, to change between longitudinal and transverse axes while keeping the target in the frame.
The patient may assist, for example, by changing position or inhaling deeply.
For the best view of an organ, image both dimensions, and tilt the probe to focus on each end.
“Mirror artifact” is expected when imaging reflective tissues such as the diaphragm. For example, in Morison pouch, mirror artifact can help rule out hemothorax or pneumothorax. When sound waves encounter the diaphragm, they do not penetrate it and thus take a longer time to reflect themselves back to the probe. The machine misinterprets this longer time as the presence of something behind the diaphragm that is actually in front of the diaphragm (you typically see a liver density behind the diaphragm on the patient’s right, or the spleen when imaging the left side). It is called mirror artifact because it mirrors what is in front of the diaphragm.
Warnings and Common Errors
Inadequate use of gel or inadequate pressure on the probe to contact the patient's skin can limit views and distort images.
Tips and Tricks
Position the patient before the examination in a way to optimize probe positioning and to maximize sonographer and patient comfort.
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الإثنين يونيو 24, 2024 12:58 pm عدل 2 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2690
نقاط : 4494
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه موضوع: رد: كل يوم معلومه أساسيه  الخميس نوفمبر 02, 2023 8:47 pm الخميس نوفمبر 02, 2023 8:47 pm | |
| Position the patient before the examination in a way to optimize probe positioning and to maximize sonographer and patient comfort.
Maneuver the probe do ultrasound imaging
Standard probe orientation: With correct placement, the right side of the patient should appear on the left side of the monitor. The probe orientation mark on one side of the probe should face the patient's right side (or cephalad if the probe is oriented longitudinally), and the marker dot on the ultrasound monitor is at the upper left corner of the ultrasound monitor.
Cardiac examination orientation: By selecting the cardiac preset, the marker dot will be on the right side of the monitor.
Coat the probe tip with ultrasound gel.
When using a covered probe, apply gel to the probe and then pull a glove or probe cover tightly over the probe tip to eliminate all air bubbles in the gel, and wrap rubber bands around the probe. Apply more gel in large amounts to the covered probe to ensure an adequate film as you move the probe.
Hold the probe and move it like a pen. Use your other fingers to stabilize the probe against the patient as you view the ultrasound monitor.
Optimize imaging. Try to avoid bone and gas, which are hyperechoic and can hide structures of interest. Gas can sometimes be pushed away. Optimize the imaging path to the target by using an acoustic window, generally through hypoechoic structures (eg, the liver when imaging the heart).
Begin by scanning large areas (sometimes called survey views) and then focus in to smaller areas of interest.
Slide the probe side-to-side or up or down, moving the probe footprint. With the footprint steady, you can tilt the probe, also called rocking, fanning, or sweeping, to give a more 3-dimensional view. You can compress the probe, pushing downward.
Rotate the probe, to change between longitudinal and transverse axes while keeping the target in the frame.
The patient may assist, for example, by changing position or inhaling deeply.
For the best view of an organ, image both dimensions, and tilt the probe to focus on each end.
“Mirror artifact” is expected when imaging reflective tissues such as the diaphragm. For example, in Morison pouch, mirror artifact can help rule out hemothorax or pneumothorax. When sound waves encounter the diaphragm, they do not penetrate it and thus take a longer time to reflect themselves back to the probe. The machine misinterprets this longer time as the presence of something behind the diaphragm that is actually in front of the diaphragm (you typically see a liver density behind the diaphragm on the patient’s right, or the spleen when imaging the left side). It is called mirror artifact because it mirrors what is in front of the diaphragm.
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الإثنين يونيو 24, 2024 1:04 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | | | كل يوم معلومه أساسيه |  |
|
مواضيع مماثلة |  |
|
| | صلاحيات هذا المنتدى: | لاتستطيع الرد على المواضيع في هذا المنتدى
| |
| |
| |
|


