
موقع د. كمال سيد الدراوي
طبي_ اكاديمي _ ثقافي _ تعليمي _ _ استشارات طبية_فيديو طبي
|
|
| | Raynaud’s disease |  |
| | | كاتب الموضوع | رسالة |
|---|
د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2688
نقاط : 4492
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: Raynaud’s disease موضوع: Raynaud’s disease  الأربعاء مارس 20, 2019 4:25 pm الأربعاء مارس 20, 2019 4:25 pm | |
| Raynaud’s diseaseRaynaud’s disease (also Raynaud, or Raynaud’s phenomenon) was first described in 1862 by Auguste Raynaud. Even at a first look, the disorder is apparent, owing to the fact that the patient notices the change in the color of their skin, particularly in their digits.At low temperatures, the skin becomes cold and pale due to abnormal vasoconstriction of the digital arterioles leading to diminished blood supply. This may result in the coldness and cyanosis of the digits as the distension of veins occurs, followed by the bluish skin coloration . With the rise of temperature, the skin turns warm and red as a result of the arterioles’ response to vasodilatation.It took quite a few years of study for complete comprehension of the pathology and physiology of Raynaud, which continues to be explained today. In 2005, Hendrik classified the causes and mechanisms of Raynaud’s phenomenon into three groups, namely:
- Vascular
- Intravascular
- Neural abnormalities
Definition of Raynaud’s DiseaseRaynaud’s disease is an exaggerated vascular response to cold temperature or emotional stress. The phenomenon is manifested clinically by sharply demarcated color changes of the skin of the digits. Reduction in the size of the blood vessels, most commonly in the fingers and toes, results in change of color from white to blue. As blood flow returns to the digits, the skin turns red.Its affection is symmetrical, usually attacks in episodes, a clear demarcated line exists between ischemic part and unaffected part.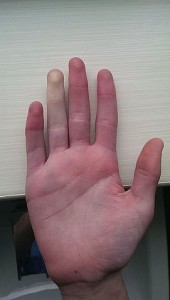
Image: “Raynaud’s Phenomenon in my right ring finger, viewed from the front of my hand. This occurs in cold weather on my fingers and my toes.” by Thomas Galvin. License: CC BY-SA 4.0 Classification of Raynaud’s DiseaseRaynaud’s disease is classified into:
- Primary Raynaud phenomenon, also known as idiopathic Raynaud disease
- Secondary Raynaud phenomenon
Primary Raynaud phenomenonPrimary Raynaud phenomenon (RP) or idiopathic Raynaud disease are terms to describe those patients without a definable cause for their vascular events. In this setting, RP is considered to be an exaggeration of normal vasoconstriction to cold exposure. Secondary Raynaud phenomenonSecondary RP refers to those patients with RP in whom an associated disease or cause may underlie the attacks. Possible associations include atherosclerosis, scleroderma, lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. It can also be a result of taking assured medications, having frostbite, smoking or using vibrating power tools for numerous years. Therefore, it is sometimes referred to as secondary Raynaud’s.Secondary Raynaud’s is more frequent than idiopathic Raynaud disease. Also, it is more likely to occur in both genders with an almost equal distribution.The disorder progresses proportionally, affecting digits from both hands or feet in symmetrical manner. Over a period of time, recurrent and sustained spasms become more common.
“Raynaud´s disease” Image created by Lecturio Symptoms of Raynaud’s DiseaseRaynaud’s disease symptoms include:
- Cold fingers or toes.
- Color changes in your skin from white, blue to red, in response to cold or stress.
- Events are episodic. Swelling, numb feeling or stinging pain upon warming or stress relief.
The disorder progresses proportionally, affecting digits from both hands or feet in symmetrical manner. Over a period of time, recurrent and sustained spasms become more common.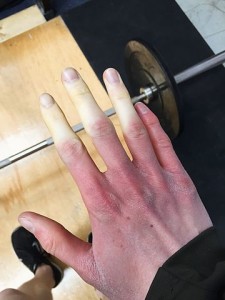
Image: “A good illustration of what Raynaud’s looks like” by Jmesy. License: CC BY-SA 4.0 Pathophysiology of Raynaud’s Disease Vascular abnormalitiesA deficit of vasodilators, mainly nitric oxide, has been suggested to be one of the cause of Raynaud’s phenomenon. Moreover, effective vasoconstrictors generally present in our endothelium (known as endothelin-1) have been observed to be flowing in elevated levels in people suffering from secondary Raynaud’s disease.Discharge of the vasoconstrictor endothelin-1 is elicited by stimuli of vasoactivation, including transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta), vasopressin and angiotensin.Angiotensin has both pro-fibrotic and vasoconstrictive impacts.In people suffering from systemic sclerosis, fundamental anomalies allied with vasculature fibrotic proliferation result in decreased blood flow toward the digits. This is a usual characteristic difference from the primary Raynaud’s disease.continuehttps://www.lecturio.com/magazine/raynauds-disease/?pc=nl&utm_source=crm&utm_medium=E-Mail&utm_campaign=dc_mk_m2_raynauds_disease&utm_content=CLC#definition-of-raynaud8217s-disease | |
|   | | | | Raynaud’s disease |  |
|
مواضيع مماثلة |  |
|
| | صلاحيات هذا المنتدى: | لاتستطيع الرد على المواضيع في هذا المنتدى
| |
| |
| |
|


