
موقع د. كمال سيد الدراوي
طبي_ اكاديمي _ ثقافي _ تعليمي _ _ استشارات طبية_فيديو طبي
|
| | | UTERUS & OVARIES |  |
| | |
| كاتب الموضوع | رسالة |
|---|
د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: UTERUS & OVARIES  السبت أبريل 20, 2024 3:39 pm السبت أبريل 20, 2024 3:39 pm | |
|  The Female PelvisThe uterus is an extraperitoneal hollow, thick-walled, muscular organ of the female reproductive tract that lies in the lesser pelvis. The Female PelvisThe uterus is an extraperitoneal hollow, thick-walled, muscular organ of the female reproductive tract that lies in the lesser pelvis.The True (or lesser) pelvis is bounded in front and below by the pubic symphysis and the superior rami of the pubis; above and behind, by the sacrum and coccyx; and laterally, by a broad, smooth, quadrangular area of bone, corresponding to the inner surfaces of the body and superior ramus of the ischium, and the part of the ilium below the arcuate line. This cavity is a short, curved canal, deeper on its posterior than on its anterior wall, and contains the pelvic inlet. Some consider this region to be the entirety of the pelvic cavity. Others define the pelvic cavity as the larger space including the false greater pelvis, just above the pelvic inlet. Greater and lesser pelvis: The greater pelvis (yellow) is larger and superior to the lesser pelvis (red) where the pelvic inlet is located. The true pelvis contains the pelvic colon, rectum, bladder, and some of the reproductive organs. The rectum is at the back, in the curve of the sacrum and coccyx; the bladder is in front, behind the pubic symphysis. In the female, the uterus and vagina occupy the interval between these viscera. The pelvic splanchnic nerves arising at S2–S4 are in the lesser pelvis. The False PelvisThe false (or greater) pelvis is bounded on either side by the ilium. In front it is incomplete, presenting a wide interval between the anterior borders of the ilia; behind is a deep notch on either side between the ilium and the base of the sacrum. Some consider this region to be part of the pelvic cavity, while others consider it part of the abdominal cavity (hence the name false pelvis). Others compromise by referring to the area as the abdominopelvic cavity. The false pelvis supports the intestines (specifically, the ileum and sigmoid colon), and transmits part of their weight to the anterior wall of the abdomen.  The uterus is an extraperitoneal hollow, thick-walled, muscular organ of the female reproductive tract that lies in the lesser pelvis.KAMALSAYED The uterus is an extraperitoneal hollow, thick-walled, muscular organ of the female reproductive tract that lies in the lesser pelvis.KAMALSAYED 
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في السبت مايو 11, 2024 12:40 pm عدل 2 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: uterus anatomy موضوع: uterus anatomy  السبت أبريل 20, 2024 4:07 pm السبت أبريل 20, 2024 4:07 pm | |
| Uterus anatomy
Key Points
Some believe that the false pelvis is actually part of the abdominal cavity and therefore that the true pelvis is the only true portion of the pelvis.
The true pelvis contains the pelvic inlet and is a short, curved canal, deeper on its posterior than on its anterior wall.
The true pelvis contains the pelvic colon, rectum, bladder, and some of the reproductive organs.
The false pelvis supports the intestines (specifically, the ileum and sigmoid colon) and transmits part of their weight to the anterior wall of the abdomen. Key Terms true pelvis: Bounded in front and below by the pubic symphysis and the superior rami of the pubis; above and behind, by the sacrum and coccyx; and laterally, by a broad, smooth, quadrangular area of bone, corresponding to the inner surfaces of the body and superior ramus of the ischium, and the part of the ilium below the arcuate line. false pelvis: Bounded on either side by the ilium; in front it is incomplete, presenting a wide interval between the anterior borders of the ilia; behind is a deep notch on either side between the ilium and the base of the sacrum UTERUS Gross anatomyThe uterus has an inverted pear shape. It measures about 7.5 cm in length, 5 cm wide at its upper part, and nearly 2.5 cm in thickness in adults ( L 7.5/ W 5/ H 2.5). It weighs approximately 3 0-40 grams. The uterus is divisible into two portions: body and cervix. About midway between (b/w) the apex and base is a slight constriction known as the isthmus. The portion above the isthmus is termed the body, and that below, the cervix. The part of the body which lies above a plane passing through the points of the entrance of the uterine tubes is known as the fundus. The body gradually narrows from the fundus to the isthmus. The cavity of the body is a mere slit, flattened anteroposteriorly. It is triangular in shape: the base being formed by the internal surface of the fundus between the orifices of the uterine tubes the apex by the internal orifice of the uterus (internal OS) through which the cavity of the body communicates with the canal of the cervix Although anatomically a part of the uterus, the uterine cervix has a different function and is associated with separate pathological entities. It is discussed in detail in a separate article. Attachments Musculotendinous and ligamentous anterior: pubocervical ligament lateral: transverse cervical ligaments (cardinal or Mackenrodt's) posterior: uterosacral ligaments inferior: puborectalis and pubovaginalis parts of the levator ani muscle Relations anteriorly: bladder; uterovesical pouch posteriorly: rectum; pouch of Douglas laterally: broad ligament; round ligament; uterine vessels uterine tubes open into its upper part inferiorly: uterine cavity communicates with that of the vagina
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في السبت مايو 11, 2024 12:55 pm عدل 3 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  السبت أبريل 20, 2024 4:16 pm السبت أبريل 20, 2024 4:16 pm | |
| | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  السبت أبريل 20, 2024 6:29 pm السبت أبريل 20, 2024 6:29 pm | |
| Position The most common position of the uterus is anteverted ( cervix angles forward) and anteflexed ( body is flexed forward): Uterine version is defined as the angle that the cervical axis makes with the vaginal axis: - anteversion: vagina-cervix angle faces anteriorly
- retroversion: vagina-cervix angle faces posteriorly
Uterine flexion is defined as the angle that the uterine body axis makes with the cervical axis: - anteflexion: cervix-body angle faces anteriorly
- retroflexion: cervix-body angle faces posteriorly
The uterus position in the adult is liable to considerable variation, depending chiefly on the condition of the bladder and rectum. When the bladder ( UB) is empty, the entire uterus is directed forward and is at the same time bent on itself at the junction of the body and cervix so that the body lies upon the bladder. As the latter fills, the uterus gradually becomes more and more erect until, with a fully distended bladder, the fundus may be directed back toward the sacrum. In the fetus, the uterus is contained in the abdominal cavity, projecting beyond the superior aperture of the pelvis. The cervix is considerably larger than the body. At puberty, the uterus is pyriform in shape and weighs from 14 to 17 g. It has descended into the pelvis, the fundus being just below the level of the superior aperture of this cavity. The palmate folds are distinct and extend to the upper part of the cavity of the organ. During menstruation, the organ is enlarged, more vascular, and its surfaces rounder; the external orifice is rounded, its labia are swollen, and the lining membrane of the body thickened, softer, and of a darker color. During pregnancy, the uterus becomes enormously enlarged, and by the eighth month, it reaches the epigastric region. The increase in size is partly due to the growth of pre-existing muscles and partly to the development of new fibers. After parturition, the uterus nearly regains its usual size, weighing about 42 g. Its cavity is larger than in the virgin state, its vessels are tortuous, and its muscular layers are more defined. The external orifice is more marked, and its edges present one or more fissures. In old age, the uterus becomes atrophied and paler and denser in texture; a more distinct constriction separates the body and cervix. The internal orifice is frequently, and the external orifice is occasionally obliterated, while the lips almost entirely disappear. https://radiopaedia.org/articles/uterus | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  السبت أبريل 20, 2024 6:40 pm السبت أبريل 20, 2024 6:40 pm | |
| | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  السبت أبريل 20, 2024 6:47 pm السبت أبريل 20, 2024 6:47 pm | |
| 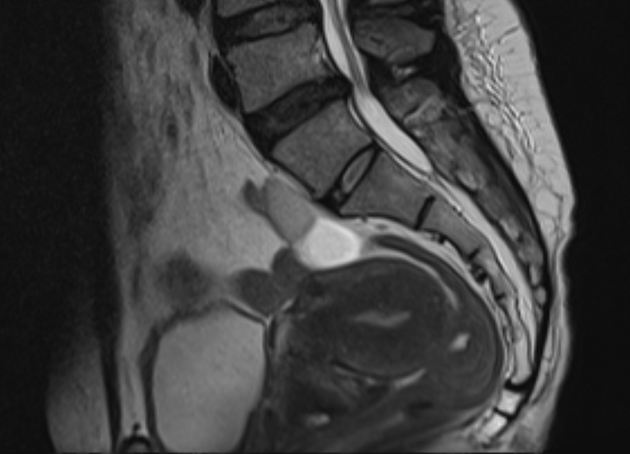 Anteverted retroflexed uterus  inverted retroflexed uterus 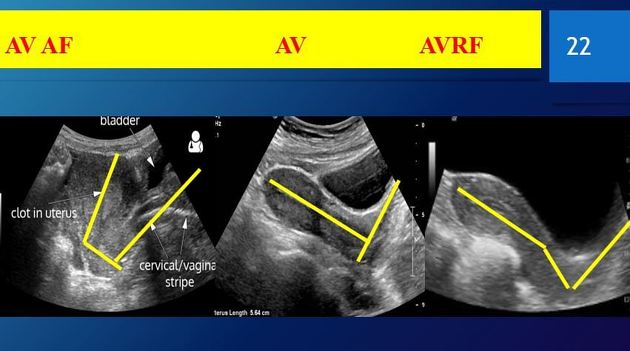 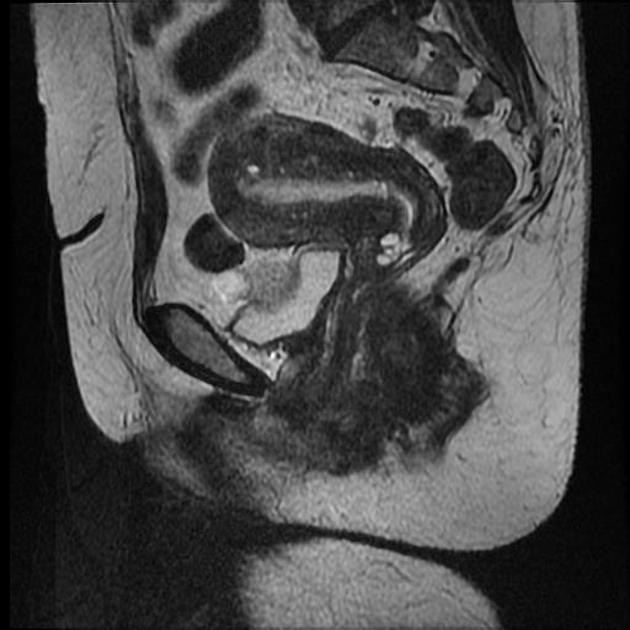 anteverted uterus  retroverted anteflexed
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في السبت أبريل 20, 2024 6:59 pm عدل 2 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  السبت أبريل 20, 2024 6:51 pm السبت أبريل 20, 2024 6:51 pm | |
| Arterial supply- uterine arteries and ovarian arteries
- the terminations of the ovarian and uterine arteries unite and form an anastomotic trunk from which branches are given off to supply the uterus
in the impregnated uterus, the arteries carry the blood to the intervillous space of the placenta
Venous drainageLymphatic drainageInnervationThe nerves are derived from the inferior hypogastric and ovarian plexuses (via the aorticorenal plexuses) from the third and fourth sacral nerves. Radiographic featuresUS is the primary diagnostic modality in characterizing uterine lesions. Meanwhile, CT scan is normally done for other non-gynecological indications. If there is indeterminate lesion found on ultrasound or CT, MRI is helpful in characterizing the uterine lesions Ultrasound The transabdominal US allows evaluation of the size and position of the uterus in the pelvic cavity. The transvaginal US allows the internal structure of the uterus to be examined | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  السبت أبريل 20, 2024 7:14 pm السبت أبريل 20, 2024 7:14 pm | |
| CT The uterus appears as a homogeneous soft tissue mass posterior to the bladder. The myometrium shows low density on unenhanced CT with the endometrial canal showing even lower density than myometrium . It normally enhances post intravenous contrast 2. There are generally three types of enhancement in a normal uterus 7: - type 1: thick or thin sub-endometrial enhancement, most commonly found in pre-menopausal women
- type 2: diffuse myometrial enhancement, found in both pre and post-menopausal women
- type 3: faint diffuse myometrial enhancement, exclusively found in post-menopausal women
There is also a possibility of patchy enhancement of the uterus. These variable enhancement patterns could be due to differences in age, parity and menstrual status. Basal layer of endometrium adjacent to the myometrium could contribute to thin sub-endometrial enhancement. Thick sub-endometrial enhancement could be due to the junctional zone. Meanwhile, diffuse myometrial enhancement could be due to the density of smooth muscles and blood vessels in the myometrium that affects the uptake of contrast 7. MRI MRI displays the zonal anatomy of the uterus. The myometrial layers are indistinguishable on T1 imaging. It can be divided into three zones on T2 weighted imaging 7: - high T2 signal of endometrium
- low T2 signal of inner myometrium, known as the junctional zone
- intermediate T2 signal of the outer myometrium
On contrasted MRI study, myometrium shows homogenous hyperintensity on arterial and venous phases. Meanwhile, endometrium enhances slowly and is more hypointense when compared to myometrium 7. There is some physiologic variability to the myometrial zonal appearance. The junctional zone is less distinct pre-menarche and during pregnancy 4. In the postmenopausal patient, the outer myometrium is thinner and of lower signal due to reduced fluid content and therefore approximates the junctional zone, with poor delineation of the margin in some patients. Myometrial zonal anatomy has diagnostic implications in the assessment of adenomyosis and in the staging of endometrial carcinoma, where the depth of myoinvasion is assessed in relation to the junctional zone. Endometrium on MRI undergoes expected physiological variation in thickness, but the structural, cyclical changes seen on ultrasound are not reproduced. https://radiopaedia.org/articles/uterusVariant anatomyMüllerian duct anomalies (MDAs) are congenital abnormalities that occur when the Müllerian ducts (paramesonephric ducts) do not develop correctly. This may be as a result of complete agenesis, defective vertical or lateral fusion, or resorption failure. https://radiopaedia.org/articles/mullerian-duct-anomalies?lang=usFluoroscopy A hysterosalpingogram (HSG) is a fluoroscopic examination of the uterus and the fallopian tubes, most commonly used in the investigation of infertility or recurrent spontaneous abortions. | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  السبت أبريل 20, 2024 7:27 pm السبت أبريل 20, 2024 7:27 pm | |
| Imaging assessment of the uterine size The uterine length is measured in the midsagittal plane from the outer serosal surface of the fundus to the external cervical os. The uterine height ( AP) is measured in the midsagittal plane anteroposteriorly ( AP) from outer to outer serosal surfaces. The uterine width ( W) is measured in the transverse plane. The uterine body length is measured in the midsagittal plane from the fundal outer serosal surface to the internal os. The uterine cervix length is measured in the midsagittal plane from the internal os to the external os. Several methods in the assessment of the uterine size are present in the literature: Uterine volume measurement 5: using the formula; Length x Width x Height x 0.523 According to this method, the normal mean uterine volume in the age of 0-1 month is 3.4 ml, in 3 months is 0.9 ml, in 1-5 years is 1 ml, in 7 years is 0.9 ml, in 9 years is 1.3 ml, in 11 years is 1.9 ml, in 13 years is 11 ml, and in 15 years is 21.2 ml Uterine length and uterine body to cervix ratio measurements 6 : - neonatal stage: length is 3.5 cm, body to cervix ratio is 1:2
- pediatric stage: length is 1-3 cm, body to cervix ratio is 1:1
- prepubertal stage: length is 3-4.5 cm, body to cervix ratio is 1-1.5: 1
- pubertal stage: length is 5-8 cm, body to cervix ratio is 1.5-2:1
- reproductive stage: length is 8-9 cm, body to cervix ratio is 2:1
- postmenopausal stage: length is 3.5-7.5 cm, body to cervix ratio is 1-1.5:1
KAMALSAYED
| |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  السبت أبريل 20, 2024 7:34 pm السبت أبريل 20, 2024 7:34 pm | |
| Related uterine pathology gamuts uterine enlargement large for dates uterus uterine restricted diffusion neoplastic malignant neoplasms involving the uterus uterine leiomyomas infections endometritis others uterine inversion incarcerated uterus adenomyosis
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في السبت مايو 11, 2024 1:16 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: OVARIES & TUBES موضوع: OVARIES & TUBES  الأحد أبريل 21, 2024 6:02 pm الأحد أبريل 21, 2024 6:02 pm | |
| Imaging Uterus Use the full urinary bladder as an acoustic window to angle across to the ovary Axial TAS image with the ovary lateral to the uterus. Axial TVS scan plane. Reposition the probe into the fornix to angle towards the adnexum. Ultrasound of Normal transvaginal ovary demonstration normal peripheral follicles. Ultrasound of The uterus may be oblique and squash the ovary giving it a flattened ovoid shape. The postmenopausal ovary can be difficult to identify because of the absence of follicles and the reduced size. The paediatric ovary will have multiple small follicles. Ovary size and volume is frequently determined with ultrasound. The volume estimate is calculated by the formula for an ellipsoid, where D 1, D 2, and D 3 are the three axial measurements: D1 x D2 x D3 x 0.52The normal, adult, non-pregnant, mean ovary volume of women who are not postmenopausal is 6-7 mL based on several studies which combined assessed tens of thousands of ovaries .. 20 20mL had been proposed as a cut-off value between normal and abnormally large, but that value was subsequently shown to be inaccurate. Values two standard deviations above the mean (to help provide a threshold for enlargement): 14-15 ml at less than 30 ys 13 ml in the 30s 11 ml in the 40s 5-6 ml in the the 50s 4-5ml above 60 ys of age Ovary volume varies normally a bit by overall body size/height. Normal ovary volume during the fertile years may be as high as 24 mL and perhaps even higher. The two ovaries may vary greatly in volume, side to side; it is not uncommon for one ovary to be twice the volume of the other. There was no significant difference in ovary volume between studies done on a mixed U.S. population versus a cohort in Nigeria. https://radiopaedia.org/articles/ovary-size-and-volume?lang=usThe normal size of a healthy ovary is 30 mm long, 25 mm wide, and 15 mm thick. In other words, the normal ovary size is 3 cm long, 2.5 cm wide, and 1.5 cm thick (0.8-12.7cc). https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-d&q=normal+ovary+ultrasound+images#vhid=fdzLZwFAg4k1cM&vssid=l
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في السبت مايو 11, 2024 1:21 pm عدل 2 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  الأحد أبريل 21, 2024 6:06 pm الأحد أبريل 21, 2024 6:06 pm | |
| | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  الأحد أبريل 21, 2024 6:09 pm الأحد أبريل 21, 2024 6:09 pm | |
| | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  الأحد أبريل 21, 2024 6:19 pm الأحد أبريل 21, 2024 6:19 pm | |
| SCAN PROTOCOL Role of Ultrasound- To examine the uterus, ovaries cervix vagina and adnexae.
- Classification of a mass identified on other modalities eg solid, cystic, mixed.
- Post surgical complications eg abscess, oedema.
- Guidance of injections, aspiration or biopsy.
- Assistance with IVF.
- To identify the relationship of normal anatomy and pathology to each other.
Indications- P/V bleeding/discharge
- Menorrhagia
- Polymenorrhea
- Amenorrhea
- Irregular periods
- Pelvic pain
- F/H uterine or ovarian Cancer
- Palpable lump
- Infertility- primary or secondary
- Anomalies
Limitations- Transvaginal scanning is contra-indicated if the patient is not yet sexually active,or cannot provide informed consent.
- Large patient habitus will reduce detail, particularly via the transabdominal approach.
- Excessive bowel gas can obscure the ovaries
| |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  الأحد أبريل 21, 2024 6:47 pm الأحد أبريل 21, 2024 6:47 pm | |
| Patient Preparation- If possible, scan the patient in the first 10 days of the cycle. Preferably Day 5-10 for improved diagnostic accuracy in the assessment of the endometrium and ovaries.
- A full bladder is required . Instruct the patient to drink 1 Litre of water to be finished 1 hour prior to their appointment. They cannot empty their bladder until after the scan.
Equipment setup- Use the highest frequency probe possible which gives adequate depth. Commonly a curvilinear 3-6Mhz probe and a 6-10Mhz endovaginal probe. Low dynamic range.
- A linear 5-12MHz probe for Paediatric patients or an ovary lying superficially.
Common PathologyVAGINAL- Gartners duct or Bartholin cyst
- Vaginal carcinoma
- Hydro/haematocolpos (secndary to imperforate hymen or vaginal stenosis)
- Foreign body
CERVICAL- Nabothian (retention) cysts
- Polyps
- Cervical fibroids
- Cervical carcinoma
- Cervical stenosis
UTERINE- Fibroids (leiomyoma)
- submucosal
- intramural
- subserosal
- pedunculated
Leiomyosarcoma
Adenomyosis
Lipoleiomyoma
ENDOMETRIAL- Endometrial Polyps
- Endometrial Carcinoma
- Endomtrial hyperplasia
- Endometritis
- Cystic hyperplasia 2ndary to Tamoxifen
- Adhesions- Ashermans Syndrome
- Submucosal fibroids
- Arterio-venous malformation (AVM)
- Hydro/haematometra
- blood/fluid/infection or retained produts of conception (RPOC)
OVARIAN- Ovarian cysts
- simple Vs complex (haemorrhagic, corpus luteal, ruptured, septated).
- any mural nodules
Dermoid
Ovarian tumours:
Cystadenoma (serous/mucinous)-Benign
Cystadenocarcinoma (serous/mucinous)-Malignant
Polycystic Ovarian Disease
Endometrioma
Torsion
Hyperstimulation syndrome
Ectopic pregnancy
POUCH OF DOUGLAS (POD) & ADNEXAE- Fluid
- Pus
- Blood
- Pelvic inflammatory disease-PID (may be indicated by above conditions)
- Cysts (Mesenteric)
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Endometriosis
- Pelvic venous congestion
FALLOPIAN TUBES- PID
- Pyosalpynx
- Hydrosalpynx
- Ecopic pregnancy
- Cyst
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Endometriosis
Bladder and Bowel should also be examined. | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  الأحد أبريل 21, 2024 6:49 pm الأحد أبريل 21, 2024 6:49 pm | |
| SCANNING TECHNIQUE TRANS-ABDOMINAL APPROACHThis is a generalised overview to identify the cervix, uterus and ovaries. - Check for the orientation the uterus (anteverted V’s retroverted)
- Assess the myometrium
- Assess the endometrial status and measure the thickness: <10mm pre menopausal; <4mm post menopause or ,<6mm if post menopausal on HRT
- Look for free fluid in the pouch of douglas
- Check the ovaries and adnexae
- Assess bladder
Scan sagittally in the midline immediately above the pubis. In this plane you should be able to assess the uterus, vagina and cervix. Zoom the image to assess and measure the endometrial thickness. Rotate into transverse and angle slightly cranially to be perpendicular to the uterus. Whilst in transverse and slightly right of midline, angle left laterally to identify the left ovary using the full bladder as an acoustic window. Examine this ovary in two planes. Now repeat this for the right ovary. TRANS-VAGINAL (TV) APPROACHINSERTING THE TV PROBE- Before letting the patient empty their bladder, show them the TV probe and explain the procedure. Indicate the length that is inserted which is approximately the length of a standard tampon. Explain there is no speculum used. Explain the importance of a TV scan because it is the gold standard in gynaecological ultrasound because of its superior accuracy and improved diagnostic resolution.
- Cover the probe with a latex free Transvaginal sheath and lubricate with sterile gel on the outside.
- Elevate the patients bottom on a thick sponge/pillow to assist the scan. A gynaecological ultrasound couch which drops down is ideal so that a better angulation is achieved for an anteverted uterus.
- Ensure the patient is ready and get permission before inserting the probe.
- If there is some resistance as the probe is being inserted, offer for the patient to help guide the probe in far enough to see the end of the fundus.
- Keep asking the patient if they are okay.
- When manouvering the probe to visualise the adnexae, withdraw slightly then angle the probe towards the fornix. This avoids unnecessary patient discomfort against the cervix.
Basic Hardcopy ImagingAn pelvic series should include the following minimum images; - Uterus – longitudinal, transverse (with measurements)
- Endometrial thickness measured in the longitudinal plane
- Cervix
- Both ovaries- longitudinal, transverse (Volume)
- Colour flow/Doppler particularly in the case of torsion
- If assessing for infertility the number of follicles should be counted and any follicles which average >9mm with 2 measurements should be documented .
- Both adnexae
- Document the normal anatomy. Any pathology found in 2 planes, including measurements and any vascularity.
Quick Links | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  الأحد أبريل 21, 2024 7:43 pm الأحد أبريل 21, 2024 7:43 pm | |
| | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  الأحد أبريل 21, 2024 8:27 pm الأحد أبريل 21, 2024 8:27 pm | |
| Endometrial Appearance• Normal premenopausal phases • Early proliferative • Mid cycle secretory • Late secretory • Post menopausal • Endometrial atrophy Endometrial hyperplasia Early proliferative5-7mm on transvaginal ultrasound Midcycle secretoryUp to 11 mm on transvaginal ultrasound Late secretory7-16mm on transvaginal ultrasound Post menopausal endometriumEndometrium should be </=4mm on transvaginal ultrasound Reasons for post menopausal
bleeding Endometrial atrophy Endometrial hyperplasia • Endometrial polyps Endometrial carcinoma Postmenopausal atrophyIf< than 4mm, postmenopausal bleeding is usually attributed to atrophy May see small amount of fluid or cystic changes Endometrial Hyperplasia• Diffuse but may not involve the entire endometrium • Histologically may +/- cellular atypia • (25% with atypia progress to cancer) • -need Bx to determine • Develops from unopposed estrogen stimulation- hormone replacement, persistent anovulatory cycles, PCO, obesity, estrogen producing ovarian cancers the acceptable range of endometrial thickness is less well established in this group, cut-off values of 8-11 mm have been suggested. the risk of carcinoma is ~7% if the endometrium is >11 mm, and 0.002% if the endometrium is <11 mm.Sep 18, 2 Tamoxifen TherapyHas estrogenic effect on postmenopausal women-causes endometrial thickening and cystic changes-Increased risk of polyps/Ca Endometrial Polyps• Localized overgrowths of endometrial tissue covered by endothelium 20% of polyps are multiple • Malignant degeneration is uncommon • May be diffuse, focal, pedunculated, stalked or contain cysts • Best evaluated with sonohysterography https://michigansonographerssociety.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/01/An-Ultrasound-Review-of-PELVIC-PATHOLOGY-True-Copy.pdf | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  الإثنين أبريل 22, 2024 12:21 pm الإثنين أبريل 22, 2024 12:21 pm | |
| Endometrial Carcinoma• Most common gynecologic malignancy occurring in 3% of women • 75-80%of this cancer occurs in postmenopausal woman • Accounts for less than 1.5% of cancer deaths in women because more than 75% of endometrial cancers are confined to the uterus. Subtypes of endometrial
cancer• Type I (80%) • Well differentiated with slow progression seen in woman 55-65 • PTEN gene mutation in 30-80% • Arises in setting of hyperplasia/elevated estrogen • Type II (20%) • Less differentiated and spreads early • in woman 65-75 • P53 mutation in up to 50% Arises in setting of endometrial atrophy Appearance of endometrial
cancerMay resemble hyperplasia/polyps with uniformed thickened echogenic endometrium More commonly the endometrium is heterogenic with poorly defined borders Endometritis• Endometrium may appear thickened, irregular and may or may not contain fluid • Gas may be seen in the endometrial canal • May occur postpartum, following surgery or with PID Endometrial Adhesions• Endometrium may appear normal on transabdominal and transvaginal US • Best seen in secretory phase when the endometrium is more hyperechoic • Sonohysterography demonstrates adhesions as bridging bands of tissue that distort the endometrial cavity Hydro/Hematometrocolpos• Accumulation of secretions and/or blood in the uterus and/or vagina with the location depending on the amount of obstruction. • When congenital due to imperforate hymen,vaginal septum,atresia, rudimentory uterine horn • When acquired due to endometrial or cervical tumors or postradiation fibrosis Intrauterine Contraceptive
Devices• Appear as echogenic linear structures in the endometrial cavity in the body of the uterus • Should see acoustic shadowing and two parallel echoes representing the anterior and posterior surfaces of the IUCD Leiomyomas, also known as ( fibroids), are a group of benign smooth muscle tumors commonly present in premenopausal women. These tumors are of monoclonal origin which arises from the smooth muscle of the uterus. Cervical Leiomyoma
Pedunculated fibroids) can prolapse into vagina)
Can be obstructive at childbirth Cervical Lesions• Nabothian cystsCommon finding Measure few mm to 4 cm May have internal echoes from hemorrhage or infection Cervical polyps Hyperechoic lesion with vascular flow Frequent cause of vaginal bleeding Cervical CarcinomaMay resemble a cervical Fibroid Usually diagnosed clinically https://michigansonographerssociety.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/01/An-Ultrasound-Review-of-PELVIC-PATHOLOGY-True-Copy.pdf | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  الإثنين أبريل 22, 2024 12:48 pm الإثنين أبريل 22, 2024 12:48 pm | |
| Endometrial hyperplasiaEndometrial hyperplasia is an abnormal proliferation of the endometrial glands and stroma, defined as diffuse smooth thickening >10 mm . One of the major concerns is the potential malignant transformation to endometrial carcinoma. EpidemiologyEndometrial hyperplasia affects women of all age groups . Clinical presentationA great majority of patients present with abnormal vaginal bleeding. PathologyHyperplasia with increased gland-to-stroma ratio; there is a spectrum of endometrial changes ranging from glandular atypia to frank neoplasia. There are several types of endometrial hyperplasia, which include: Hyperplasia can be also classified into two broad groups 5: Associations Unopposed estrogen stimulation (either from an endogenous or exogenous source) is implicated in its pathogenesis; some of these conditions include: tamoxifen
Ultrasound
Imaging the endometrium on days 5-10 of a woman's cycle reduces the variability in endometrial thickness.
premenopausal
normal endometrial thickness depends on the stage of the menstrual cycle, but a thickness of 15 mm is considered the upper limit of normal in the secretory phase
hyperplasia can be reliably excluded in patients only when the endometrium measures less than 8 mm 15
postmenopausal
a thickness of >5 mm is considered abnormal
The appearance can be non-specific and cannot reliably allow differentiation between hyperplasia and carcinoma 5. Usually, there is a homogeneous smooth increase in endometrial thickness, but endometrial hyperplasia may also cause asymmetric/focal thickening with surface irregularity, an appearance that is suspicious for carcinoma. Cystic changes can also be seen in endometrial hyperplasia. Ultrasound features that are suggestive of endometrial carcinoma as opposed to hyperplasia include 13: - heterogeneous and irregular endometrial thickening
- polypoid mass lesion
- intrauterine fluid collection
- frank myometrial invasion
Treatment and prognosisUp to one-third of endometrial carcinoma is believed to be preceded by endometrial hyperplasia, therefore a biopsy is required for a definitive diagnosis.
Because endometrial hyperplasia has a non-specific appearance, any focal abnormality should lead to biopsy if there is clinical suspicion for malignancy (e.g. vaginal bleeding).
Differential diagnosisOn ultrasound, appearances can potentially simulate:
- normal thickening during the secretory phase: see endometrial thickness
- sessile endometrial polyp(s): may contain cystic spaces 4
- submucosal uterine fibroids
- endometrial cancer
- adherent intrauterine blood clot
- pregnancy (including ectopic pregnancy)
- incomplete abortion 14
ALSO SEE abnormal endometrial thickening question quiz https://radiopaedia.org/articles/abnormally-thickened-endometrium-differential-1?lang=us | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  الإثنين أبريل 22, 2024 12:54 pm الإثنين أبريل 22, 2024 12:54 pm | |
| | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES موضوع: رد: UTERUS & OVARIES  الإثنين أبريل 22, 2024 1:21 pm الإثنين أبريل 22, 2024 1:21 pm | |
| The endometrium refers to the inner lining of the uterine lumen, composed of endometrial glands surrounded by loose highly cellular connective tissue. Gross anatomyLayers In women of reproductive age, the endometrium is composed of two layers: - stratum basale (basal layer):
- describes the deeper one-third supporting layer of the endometrium that adheres to the myometrium
- after the superficial two-thirds of the endometrium (stratum functionale) are shed during menstruation, the stratum basale remains to regenerate the endometrium ready for the next cycle
stratum functionale (functional layer):
describes the superficial two-thirds that proliferates, secretes and then sheds during the menstrual cycle (in the absence of pregnancy) in response to hormonal factors
proliferation of the functional layer of the endometrium is predominantly stimulated by estrogen
There is no discrete border between the two layers, however, the layers are distinguishable because stromal tissue is more cellular in the basal layer. If pregnancy occurs, the endometrium is not shed but remains as the =decidua&lang=us]decidua. Blood supplyArterial supply - branches of the uterine and ovarian arteries that perforate through the myometrium
- upon the decrease in progesterone before menstruation, the arteries supplying the functional layer of the endometrium constrict, leading to ischemia and shedding
Venous drainage Lymphatic drainagePara-aortic, internal iliac and external iliac nodes via lymphatic vessels through the myometrium. Radiographic featuresThe endometrium is generally assessed by ultrasound or MRI examination. UltrasoundWomen of reproductive age:- day 1 to 4 of the menstrual cycle: hyperechoic line measuring 1 to 4 mm
- early proliferative phase (day 5 to 13): hyperechoic line measuring 5 to 7 mm
- late proliferative phase (day 14 to 16): multilayered appearance with hypoechoic functional layer and hyperechoic basal layer, as well as a thin central hyperechoic layer representing overlapped or interfacing opposed layers; typically less than 11 mm
- secretory phase (day 16 to 28): thickened hyperechoic endometrium measuring up to 16 mm
Postmenopausal women: - regular, thin hyperechoic line measuring up to 5 mm, representing the remaining basal layer of endometrium
Please see the separate article on endometrial thickness for a detailed discussion of measurements and pathological correlation . Related pathology | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: Endometrial polyp موضوع: Endometrial polyp  الإثنين أبريل 22, 2024 5:27 pm الإثنين أبريل 22, 2024 5:27 pm | |
| Endometrial polyp Endometrial polyps are benign nodular protrusions of the endometrial surface, and one of the entities included in a differential of endometrial thickening. Endometrial polyps can either be sessile or pedunculated. They can often be suggested on ultrasound or MRI studies but may require sonohysterography or direct visualization for confirmation. EpidemiologyThe prevalence of endometrial polyps increases with age and ranges from 8-35% 8. Risk factors - patients receiving tamoxifen
- endometriosis: 2.8x increased risk 12
- foreign bodies
- multiparity
- chronic cervicitis
- estrogen secretion
Clinical presentationMost polyps are asymptomatic although they can be a common cause of postmenopausal bleeding (can account for ~30% of cases of PMB 5). In premenopausal women, they may cause intermenstrual bleeding, metrorrhagia, and infertility. PathologyPolyps can be histologically characterized as localized hyperplastic overgrowths of glands and stroma. They consist of irregularly-distributed endometrial glands and stroma and generally consist of three components: - a stroma of focally or diffusely dense fibrous or smooth muscle tissue
- thick-walled vessels
- endometrial glands
2.5%of endometrial polyps (range 0.8-4.8%) are premalignant or malignant 9 An adenomyomatous endometrial polyp is a pedunculated variant comprising of smooth muscle tissue in addition to the usual endometrial glands and stroma. Location- there is a predilection towards the fundal and cornual regions within the uterus
- they can be multiple in ~20% of cases
- rarely protrude into the endocervical canal or through the cervical os
- Ultrasound
The best time of examination for endometrial polyp is postmenstrual.
- usually solitary homogeneous and echogenic lesion
- =interrupted-mucosa-sign&lang=us]interrupted mucosa sign 10: the endometrial polyp focally interrupts the normal mucosal contour of the uterine cavity
- it is rarely hypoechoic or heterogeneous
- a stalk to the polyp may either be thin (i.e. pedunculated) or broad-based
- the =bright-edge-sign&lang=us]bright edge sign 11: the appearance of one or two well-defined short echogenic linear echoes at the polyp borders which are perpendicular to the ultrasound beam
- may appear isoechoic as a focal non-specific thickened endometrium, without visualization of a discrete mass
- can rarely appear as diffuse endometrial thickening as the endometrial polyp fills the endometrial cavity, mimicking endometrial hyperplasia
- rarely cystic spaces could be seen corresponding to dilated glands filled with proteinaceous fluid within the
- polyp
- may be surrounded by endometrial fluid
Color Doppler- feeding artery sign: a single feeding vessel may be seen extending to the polyp on color Doppler imaging 7
- visualization of a vascular pedicle is 76% sensitive and 95% specific for endometrial polyps 7
3D ultrasound- 3D ultrasound may be useful to help delineate the borders of a polyp
Sonohysterography Although not always necessary for a diagnosis, polyps are well-characterized on sonohysterography and appear as echogenic, smooth, intracavitary masses outlined by the fluid. The typical appearance of an endometrial polyp at sonohysterography is 1/ a well-defined, 2/ homogeneous, 3/ polypoid lesion that is 4/ isoechoic to the endometrium with preservation of the endometrial-myometrial interface 5. 5/ There is usually a well-defined vascular pedicle within the stalk. Treatment and prognosisMost polyps are benign and may be treated with a polypectomy, if symptomatic. ComplicationsDifferential diagnosisEntities that can potentially mimic an endometrial polyp include: For hyperechoic content within the endometrium also consider: | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: Endometrial polyp موضوع: Endometrial polyp  الإثنين أبريل 22, 2024 5:38 pm الإثنين أبريل 22, 2024 5:38 pm | |
|  endom polyp 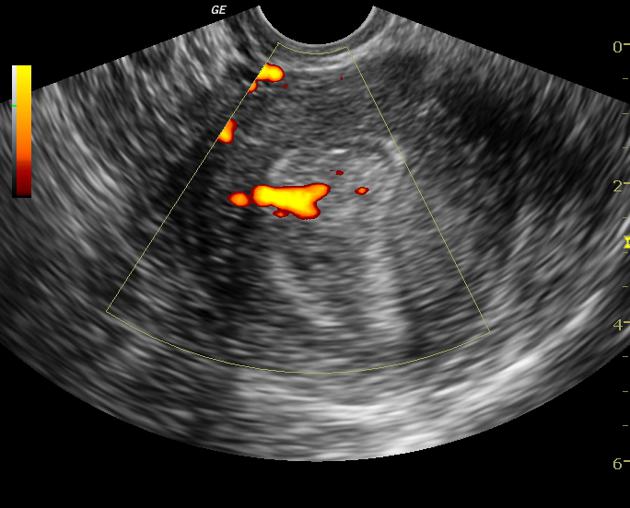 endom polyp  endom polyp 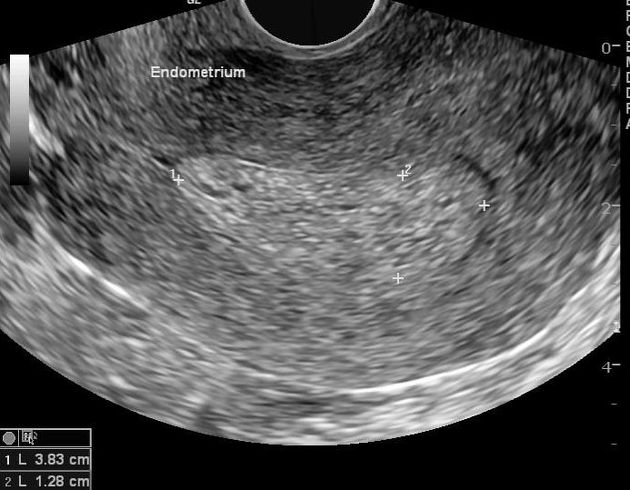 endom polyp 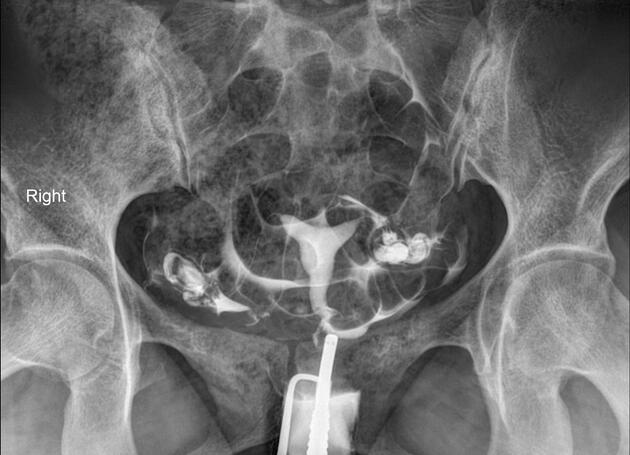 endom polyp by hysterosalpingogram
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في الثلاثاء أبريل 23, 2024 4:20 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | د.كمال سيد
Admin




عدد المساهمات : 2463
نقاط : 4251
السٌّمعَة : 9
الجنس : 
علم بلدك : 
تاريخ الميلاد : 03/04/1950
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/07/2012
العمر : 74
الموقع : السودان - سنار
العمل/الترفيه : طبيب عمومى وموجات صوتية
الساعة الان :
دعائي : 
 |  موضوع: Endometriosis موضوع: Endometriosis  الإثنين أبريل 22, 2024 6:01 pm الإثنين أبريل 22, 2024 6:01 pm | |
| EndometriosisEndometriosis is a common, chronic gynecological condition defined as the presence of functional endometrial glands and stroma-like lesions outside the uterus. It manifests in three ways: 1/ superficial (peritoneal) disease, 2/ ovarian disease ( endometriomas), 3/ and deep endometriosis. Endometriosis is highly associated with adenomyosis (in which endometrial tissue is confined to the uterine musculature). Size varies, ranging from microscopic endometriotic implants to large cysts ( endometriomas) and nodules. Deep infiltrating endometriosis is complex and surgically challenging. EpidemiologyTypically endometriosis presents in young women, with a mean age of diagnosis of 25-29 years 4, although it is not uncommon among adolescent girls. Up to 5% of cases are diagnosed in postmenopausal women. Potential risk factors include family history and short menstrual cycles. Racial predisposition remains controversial 5,7. It is difficult to ascertain the overall prevalence of endometriosis, but in women who underwent laparoscopy for various reasons, the prevalence was as follows 5,39: - asymptomatic women (laparoscopy for tubal ligation): ~5% (range 1-10%)
- primary infertility: ~35% (range 17-50%)
- pelvic pain: ~12.5% (range 5-21%)
Clinical presentationSymptoms pelvic pain
including dyspareunia, cyclical dysmenorrhea, chronic pelvic pain, abdominal pain 39
usually pelvic pain is associated with menses (cyclical pain) but pain may not be cyclical 12
unusual symptoms
gastrointestinal involvement: catamenial diarrhea ( catamenial : signs, symptoms, or conditions that only occur when a person is having a menstrual period.), rectal bleeding and constipation
small bowel obstruction can occur in 7-23% of patients with intestinal involvement 36
bladder involvement: urgency, frequency, hematuria
thoracic involvement: pleuritic chest pain, pneumothorax, pleural effusions or cyclic hemoptysis
asymptomatic
especially if the disease is isolated to the peritoneum
stage of disease does not necessarily correlate with the severity of the symptoms 16
MORE......
KAMALSAYED
عدل سابقا من قبل د.كمال سيد في السبت مايو 11, 2024 1:50 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|   | | | | UTERUS & OVARIES |  |
|
مواضيع مماثلة |  |
|
| | صلاحيات هذا المنتدى: | لاتستطيع الرد على المواضيع في هذا المنتدى
| |
| |
| |
|


